Fault Activity Map of California. California Department of Conservation.
A History of Earthquake Safety: California’s 100-year Learning Curve — Optimum Seismic
Search Earthquakes Near You ( Relative2Me ). Brown lines are known hazardous faults and fault zones. Magnitude = ? for new earthquakes until a magnitude is determined (takes 4-5 minutes). Maps are updated within 1-5 minutes of an earthquake or once an hour. (Smaller earthquakes in southern California are added after human processing, which may

Source Image: hpcwire.com
Download Image
The California Geological Survey’s Earthquake Hazards Zone Application (EQ Zapp) is an interactive map that details the risk of earthquakes and related hazards for different areas of the state. The map is searchable by address, and it maps three main hazard zones: Fault zones Landslide zones Liquefaction zones The map also displays areas that have not yet been evaluated for liquefaction or

Source Image: geology.utah.gov
Download Image
Map of faults in southern California | U.S. Geological Survey USGS scenarios project more than 1,800 deaths, and 50,000 injuries due to a major Southern San Andreas fault earthquake. CoreLogic, a business analysis service, estimated a Southern San Andreas fault rupture will cause 3.5 million homes to be at risk with $289 billion in reconstruction value. Twelve years ago, seismologists modeled how the

Source Image: scedc.caltech.edu
Download Image
Map Of Earthquake Fault Lines In California
USGS scenarios project more than 1,800 deaths, and 50,000 injuries due to a major Southern San Andreas fault earthquake. CoreLogic, a business analysis service, estimated a Southern San Andreas fault rupture will cause 3.5 million homes to be at risk with $289 billion in reconstruction value. Twelve years ago, seismologists modeled how the Fault Activity Map of California Application. Explore the interactive map of active faults and fault zones in California, based on the latest data from the California Geological Survey and the USGS. Learn about the potential hazards and risks of living near fault lines.
Southern California Earthquake Data Center at Caltech
Detailed Description. Map of faults in southern California. Bold numbers show the average time between big earthquakes, determined at paleoseismic sites (triangles). Thick red lines show the extent of historic ruptures. Mapping Fault-Lines in Earthquake Maps | Musings on Maps

Source Image: dabrownstein.com
Download Image
Diagram of California earthquake probabilities – Stock Image – E365/0040 – Science Photo Library Detailed Description. Map of faults in southern California. Bold numbers show the average time between big earthquakes, determined at paleoseismic sites (triangles). Thick red lines show the extent of historic ruptures.

Source Image: sciencephoto.com
Download Image
A History of Earthquake Safety: California’s 100-year Learning Curve — Optimum Seismic Fault Activity Map of California. California Department of Conservation.

Source Image: optimumseismic.com
Download Image
Map of faults in southern California | U.S. Geological Survey The California Geological Survey’s Earthquake Hazards Zone Application (EQ Zapp) is an interactive map that details the risk of earthquakes and related hazards for different areas of the state. The map is searchable by address, and it maps three main hazard zones: Fault zones Landslide zones Liquefaction zones The map also displays areas that have not yet been evaluated for liquefaction or

Source Image: usgs.gov
Download Image
San Andreas-like fault found in eastern U.S. In California, the known active surface faults are classified in the 1997 Uniform Building Code as A faults, B faults and C faults. An A fault is the most destructive and a C fault is the least destructive. Only the A and B faults are included in the probabilistic maps. The slip rate and maximum magnitude of earthquakes associated with a fault
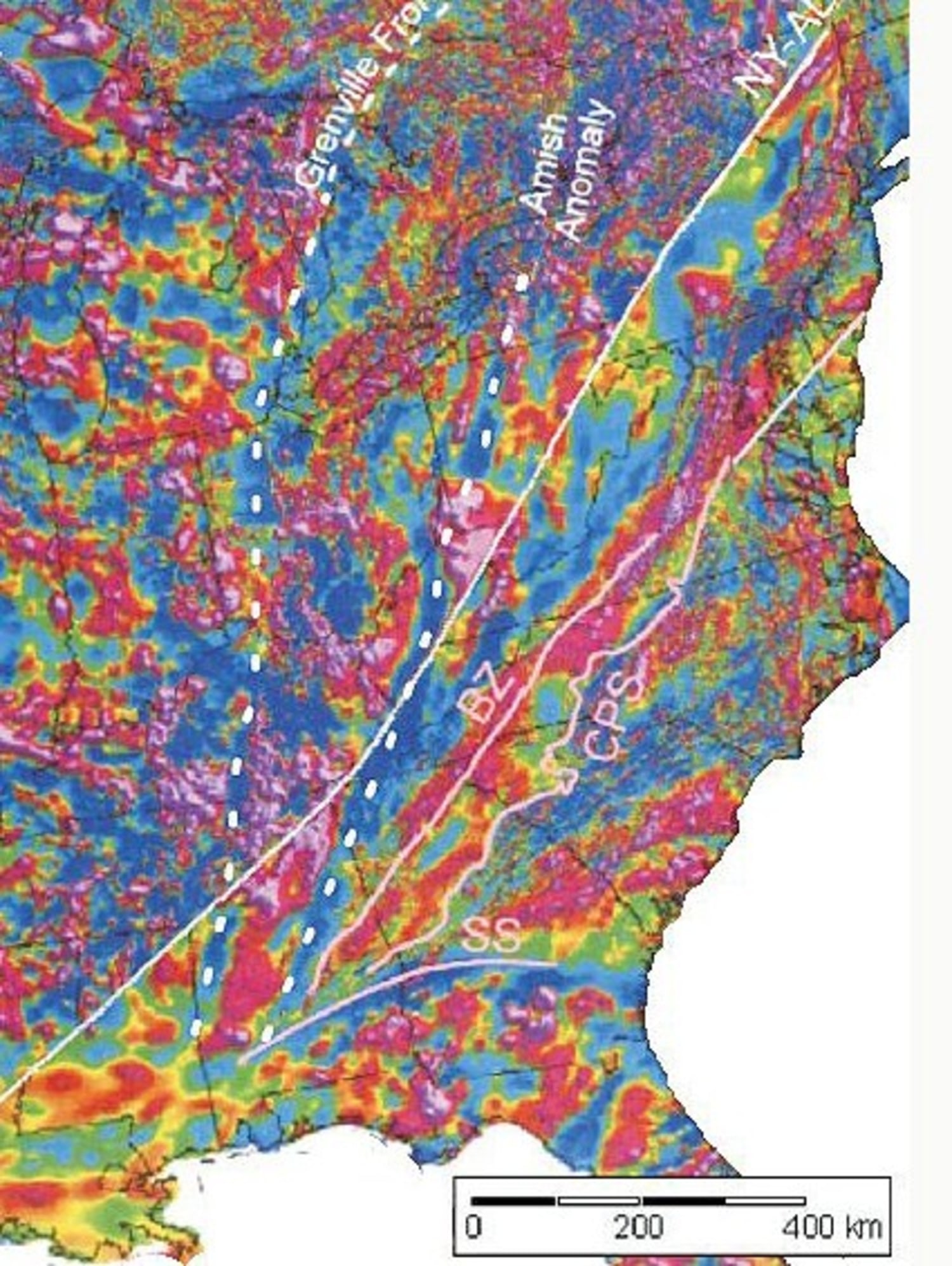
Source Image: nbcnews.com
Download Image
New Earthquake Fault Maps Released for Napa Area – HomeGuard USGS scenarios project more than 1,800 deaths, and 50,000 injuries due to a major Southern San Andreas fault earthquake. CoreLogic, a business analysis service, estimated a Southern San Andreas fault rupture will cause 3.5 million homes to be at risk with $289 billion in reconstruction value. Twelve years ago, seismologists modeled how the
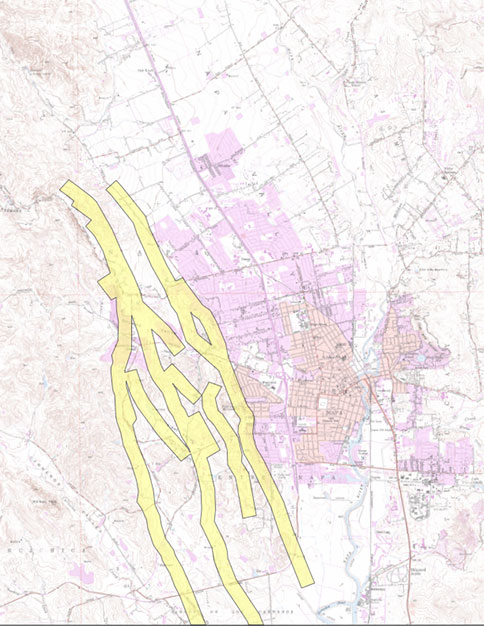
Source Image: homeguard.com
Download Image
Pinterest Fault Activity Map of California Application. Explore the interactive map of active faults and fault zones in California, based on the latest data from the California Geological Survey and the USGS. Learn about the potential hazards and risks of living near fault lines.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Diagram of California earthquake probabilities – Stock Image – E365/0040 – Science Photo Library
Pinterest Search Earthquakes Near You ( Relative2Me ). Brown lines are known hazardous faults and fault zones. Magnitude = ? for new earthquakes until a magnitude is determined (takes 4-5 minutes). Maps are updated within 1-5 minutes of an earthquake or once an hour. (Smaller earthquakes in southern California are added after human processing, which may
Map of faults in southern California | U.S. Geological Survey New Earthquake Fault Maps Released for Napa Area – HomeGuard In California, the known active surface faults are classified in the 1997 Uniform Building Code as A faults, B faults and C faults. An A fault is the most destructive and a C fault is the least destructive. Only the A and B faults are included in the probabilistic maps. The slip rate and maximum magnitude of earthquakes associated with a fault